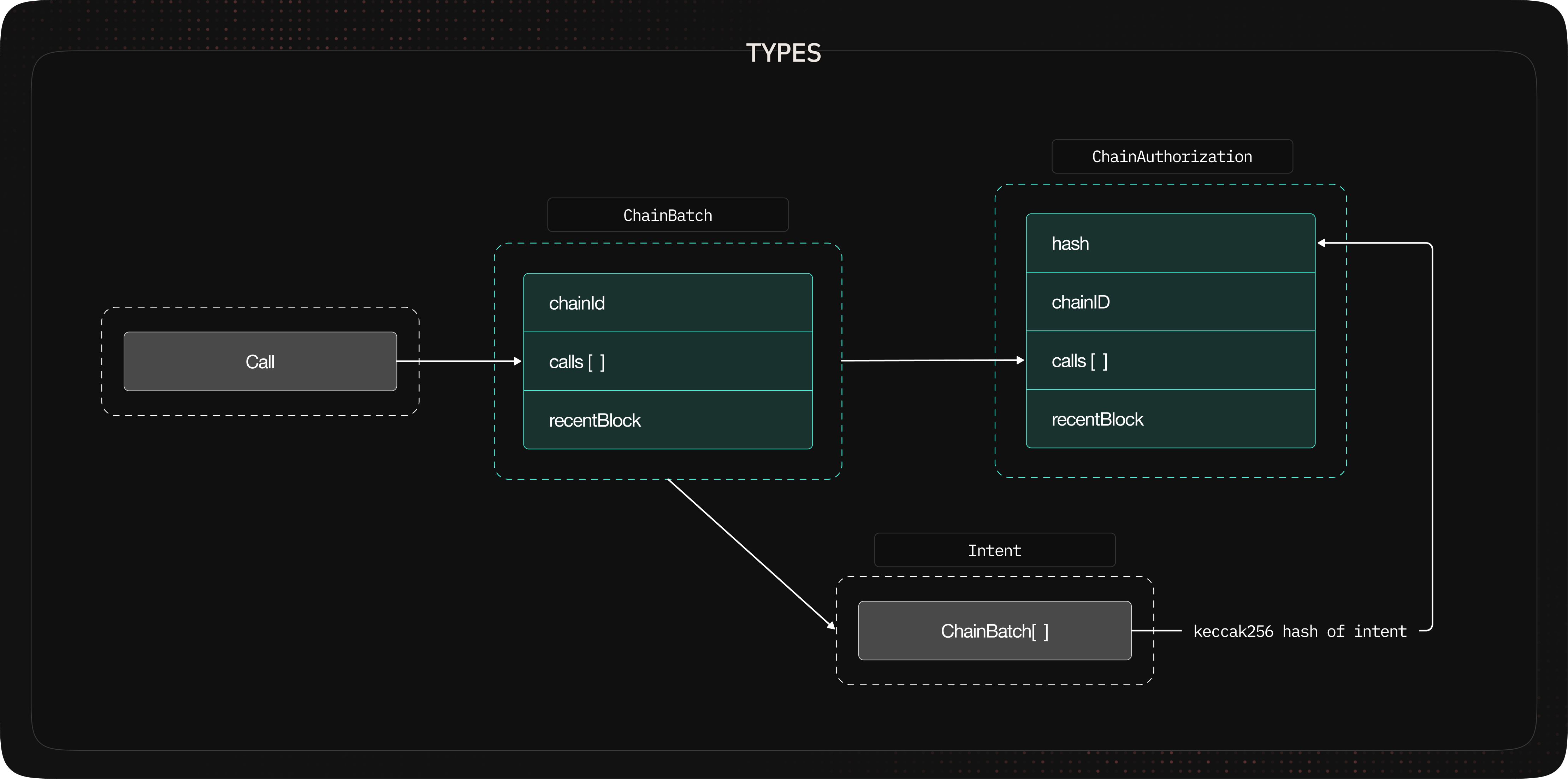
Naming Convention
The API uses the following naming convention:- Intent: The parent action which contains ChainBatch(es)
- ChainBatch: For a specific chain, and has many Call(s)
- Call: Has
to,data, andvalueparameters
Process Flow

Delegate contract, see our deep dive on EIP-7702 and Delegate Contract.
What Actually Happens
1. Transaction Submission
When you callPOST /transaction/submit:
- Transaction Validation: API validates the transaction structure and authorization array
- Database Storage: Intent and authorization data is saved to the database
- Chain Broadcast: Transaction is broadcast to the appropriate blockchain
- Response: Returns transaction hash and intent ID for tracking
2. Intent Execution
When you callPOST /intent/{intentId}/execute/{stepId}:
- Step Lookup: Retrieves the specific step from the database using intent ID and step index
- Execution Trigger: Performs the actual work for that step (checks, transactions, etc.)
- Result Capture: Records execution results and any transaction hashes
- Response: Returns execution status and results
Technical Implementation
Intent Structure
Step Execution Model
Transaction Submit Request Structure
Key Concepts
Intent ID Generation
- The intent ID is the signature of the chainBatches
- This approach is similar to Solana’s transaction ID system
- Provides a unique, deterministic identifier for each intent
Step Index System
- Steps are indexed as integers:
[0, n)where n = chainBatches.length - Step 0 = first chain authorization, Step 1 = second, etc.
- Steps must be executed sequentially in order
Authorization Array
- Multiple Authorizations: Can submit multiple EIP-7702 authorizations in a single transaction
- Cross-Chain Support: Each authorization can be for different chains or addresses
- Flexible Delegation: Supports complex multi-chain execution patterns
Execution Model
- Active Execution: Calling the POST endpoint triggers actual work
- Unit of Work: Each step call performs one discrete operation
- Stateful: Execution state is persisted in the database
- Resumable: Failed or interrupted intents can be resumed
Error Handling
The API implements comprehensive error handling:- 400 Bad Request: Invalid transaction format, malformed parameters, or out-of-range step IDs
- 404 Not Found: Intent not found or step index exceeds available steps
- 500 Internal Server Error: Database errors, chain communication failures, or execution errors
Data Persistence
Unlike the current in-memory implementation:- Database Storage: All intent data is persisted to database
- Reliable Execution: Steps can be retried if they fail
- Audit Trail: Complete execution history is maintained
- Recovery: System can recover from restarts without losing state
Monitoring
Comprehensive monitoring capabilities:- Database Logging: All operations are logged to database
- Execution Tracking: Detailed step-by-step execution results
- Transaction Hashes: All on-chain transactions are tracked
- Status Endpoints: Real-time status via API calls
